Breadth-first search
In breadth-first search (BFS) traversal starts from a single node, and the order of visited nodes is decided based on nodes' distance from the source node. This means that when a certain node is visited, it can be safely assumed that all nodes that are fewer relationships away from the source node have already been visited, resulting in the shortest path from the source node to the newly visited node.
- Graph
- Python code
- Output
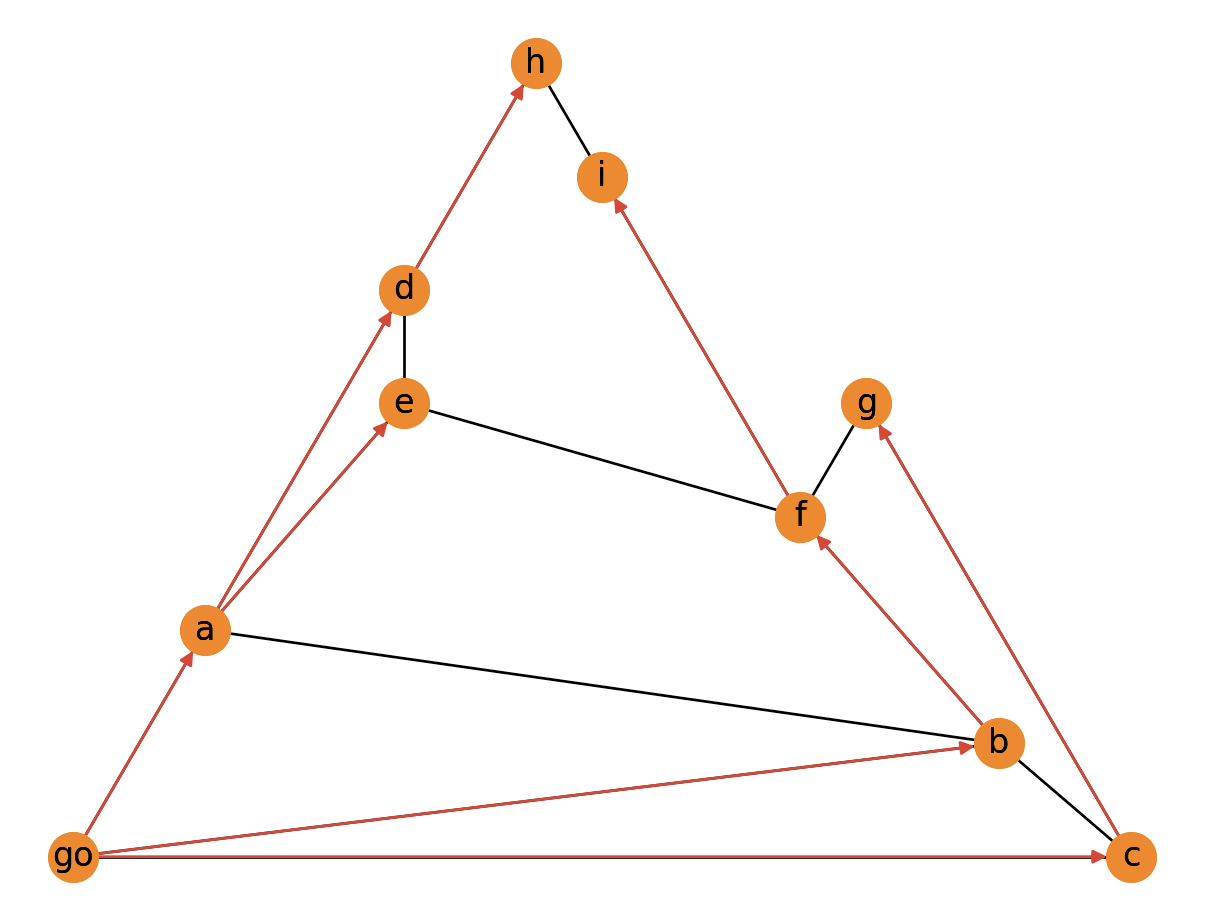
Let's say you have a graph in the graph.txt file:
go a
go b
go c
a d
a e
a b
b f
b c
c g
d h
d e
e f
f i
g f
h i
Then you can read the graph, calculate shortest paths with breadth-first search algorithm and draw the results:
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
with open("graph.txt") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
edgeList = [line.strip().split() for line in lines]
g = nx.Graph()
g.add_edges_from(edgeList)
pos = nx.planar_layout(g)
nx.draw(g, pos, with_labels=True, node_color="#f86e00")
bfs = nx.bfs_tree(g, source="go")
nx.draw(bfs, pos, with_labels=True, node_color="#f86e00", edge_color="#dd2222")
plt.show()
Where to next?
There are many graph algorithms libraries out there, with their own implementations of breadth-first search algorithm. NetworkX's algorithms are written in Python, and there are many other libraries that offer faster C++ implementations, such as MAGE, a graph algorithms library developed by Memgraph team.